Degree Requirement
To earn the bachelor’s degree, students must complete a minimum of 128 credits. The curriculum is structured to provide both a strong foundation in statistics and data science as well as the flexibility to pursue broader academic interests. Of the total credits required:
• 84 credits must be earned through required courses that establish the core knowledge and skills in the major.
• 16 credits must come from departmental electives offered within the Department of Statistics and Data Science, allowing students to explore advanced topics and specialized areas of study.
• 28 credits may be taken as electives from other departments, giving students the opportunity to complement their major with coursework in fields such as mathematics, computer science, economics, the social sciences, or other disciplines of interest.
This distribution ensures that graduates develop both the technical expertise necessary for careers in statistics and data science and the intellectual breadth characteristic of a well-rounded undergraduate education.
Required Courses
Details of the required courses are provided below.
|
Required Courses for the B.S. degree in Statistics and Data Science (enrollment in 2025) |
|||||||||||
|
Course Title |
Credit |
Year 1 |
Year 2 |
Year 3 |
Year 4 |
Remarks |
|||||
|
F |
S |
F |
S |
F |
S |
F |
S |
||||
|
Fundamental Courses: 12 credits |
|||||||||||
|
Foreign Language (Q) |
8 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
Four credits for English and four credits for other foreign languages |
|||||
|
Ability of Expressing in Spoken and Written Chinese |
2 |
||||||||||
|
Learning in University |
1 |
1 |
Learning and Development (N) |
||||||||
|
Learning and Practice of Clubs: An introduction |
1 |
1 |
|||||||||
|
General Education and Core Courses: 12 credits (7 credits as required, 5 credits as selective) |
|||||||||||
|
Exploring Sustainability |
1 |
1 |
|||||||||
|
Appreciation of Chinese Literature (L) |
2 |
Humanities Field: 2 Credits required (1 out of 4 categories) |
|||||||||
|
History Studies (P) |
2 |
||||||||||
|
Philosophy and Religion (V) |
2 |
||||||||||
|
Arts Appreciation and Invention (M) |
2 |
||||||||||
|
Global Outlook (T) |
2 |
Social Field: 2 Credits required (1 out of 4 categories) |
|||||||||
|
Futures Studies (R) |
2 |
||||||||||
|
Social Analysis (W) |
2 |
||||||||||
|
Civil Society and Participation (S) |
2 |
||||||||||
|
Information Education (O) |
2 |
Scientific Field: 2 Credits required (1 out of 3 categories) |
|||||||||
|
Global Technology Revolution (Z) |
2 |
||||||||||
|
Natural Sciences (U) |
2 |
||||||||||
|
Service and Activity Courses: 2 credits |
|||||||||||
|
Physical Education |
4 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
Excluded from graduation credits |
|||||
|
All-Out Defense Education Military Training(I)—National Defense Technology |
1 |
1 |
|
Excluded from graduation credits |
|||||||
|
Campus and Community Service-Learning |
2 |
1 |
1 |
|
|||||||
|
Professional Courses: 58 credits |
|||||||||||
|
Digital Technology and AI Application |
4 |
2 |
2 |
Two credits of Information Education can be waived. |
|||||||
|
Statistics |
4 |
4 |
|||||||||
|
Advanced Statistics |
4 |
4 |
|||||||||
|
Calculus |
4 |
2 |
2 |
||||||||
|
Economics |
4 |
2 |
2 |
||||||||
|
Accounting |
4 |
2 |
2 |
||||||||
|
Management |
3 |
3 |
|||||||||
|
Introduction to Probability Theory |
4 |
2 |
2 |
||||||||
|
Linear Algebra |
4 |
2 |
2 |
||||||||
|
SAS Programming |
3 |
3 |
|||||||||
|
R Programming |
3 |
3 |
|||||||||
|
Survey Sampling |
3 |
3 |
|||||||||
|
Design of Experiments |
3 |
3 |
|||||||||
|
Mathematical Statistics |
6 |
3 |
3 |
||||||||
|
Regression Analysis |
3 |
3 |
|||||||||
|
Multivariate Analysis |
3 |
3 |
|||||||||
|
Machine Learning |
3 |
3 |
|||||||||
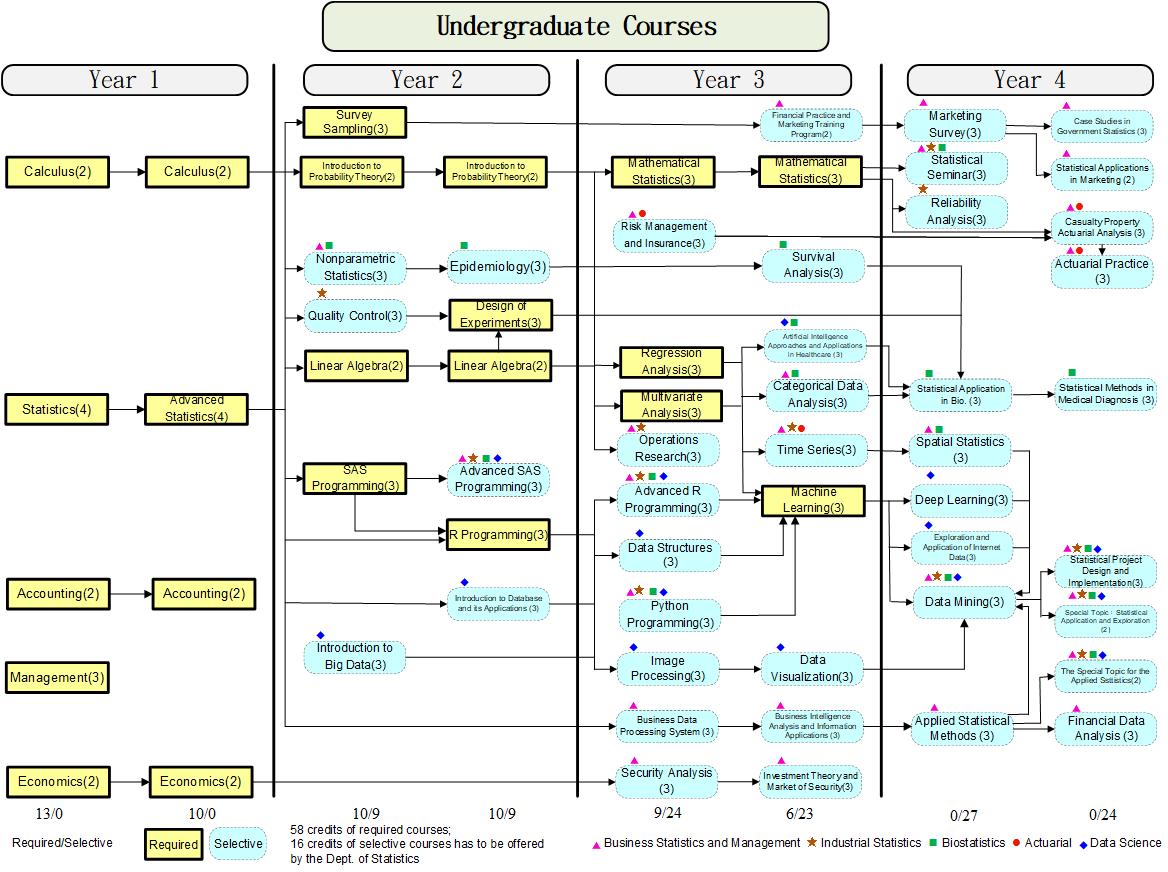
Course Tree
The diagram illustrates the structure of the undergraduate courses. An arrow from course A to course B indicates that course A is normally taken before course B. For example, students often take Statistics before advancing to Advanced Statistics, or complete Regression Analysis before moving on to Time Series, Categorical Data Analysis, and Machine Learning.